今天我们要讲解是一个布局组件:LinearLayout(线性布局),LinearLayout 是一个视图组,用于使所有子视图在单个方向(垂直或水平)保持对齐。
LinearLayout 的所有子视图依次堆叠,因此无论子视图有多宽,垂直列表每行均只有一个子视图,水平列表将只有一行高(最高子视图的高度加上内边距)。LinearLayout 会考虑子视图之间的边距以及每个子视图的对齐方式(右对齐、居中对齐或左对齐)。
我们在屏幕适配中用的比较多的就是 LinearLayout 的 weight(权重属性) ,在这一节里,我们会详细地解析 LinearLayout,包括一些基本的属性、weight属性的使用,divider绘制下划线等特性。
# 常用属性
线性布局的常用属性有:
id: 为该布局组件设置一个资源id,可以在使用的时候通过这个资源id获取到这个组件的对象。layout_width:布局的宽度,可以是一个固定大小值,也可以指定计算方式,自行计算宽度,有match_parent(填满父容器),wrap_content(根据自身组件实际大小)两种计算方式。layout_height:布局的高度,可以是一个固定大小值,也可以指定计算方式,自行计算宽度,有match_parent(填满父容器),wrap_content(根据自身组件实际大小)两种计算方式。orientation:布局的排列方向,有horizontal(水平方向),vertical(垂直方向,默认方向)。layout_gravity:控制自身组件在父容器中的对齐方式。gravity:控制组件内包含的子元素的对齐方式,如left,right,top,bottom,center等等,还可以组合使用,如:left|top。backgroud:设置组件的背景,可以指定一个图片资源也可以是颜色资源。
如果需要了解更多属性,请参考官方API (opens new window)。
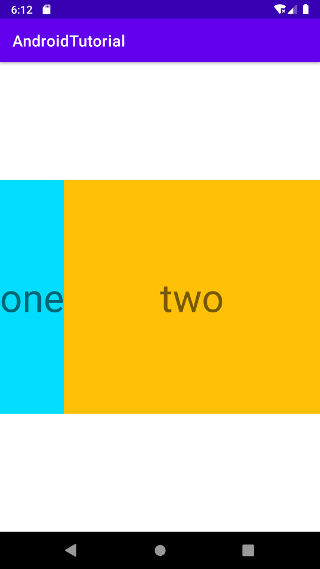
# 水平方向布局
orientation属性为 horizontal ,让子元素组件水平方向上布局,并且设置 gravity 为 center,让子元素组件相对布局容器居中对齐。
布局文件实现代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/ll_demo"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:background="#00ddff"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="one"
android:textSize="50sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:background="#FFC107"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="two"
android:textSize="50sp" />
</LinearLayout>
最终效果图:
# 垂直方向布局
orientation属性为 vertical ,让子元素组件垂直方向上布局,并且设置 gravity 为 center,让子元素组件相对布局容器居中对齐。
布局文件实现代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/ll_demo"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:background="#00ddff"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="top"
android:textSize="50sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:background="#FFC107"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="bottom"
android:textSize="50sp" />
</LinearLayout>
最终效果图:

# 权重布局
weight 布局权重属性是在屏幕适配中最常使用的属性,顾名思义,就是将子部件按照一定的权重配置的比例进行水平方向或者垂直方向布局。
LinearLayout 使用 android:layout_weight 属性向视图分配“权重”值。如果拥有更大的权重值,视图便可展开,填充父视图中的任何剩余空间。子视图可指定权重值,然后系统会按照子视图所声明的权重值比例,为其分配视图组中的任何剩余空间。默认权重为零。
# 均等分布
如要创建线性布局,让每个子视图使用大小相同的屏幕空间,请将每个子视图的 android:layout_height 设置为 "0dp"(针对垂直布局),或将每个子视图的 android:layout_width 设置为 "0dp"(针对水平布局)。然后,请将每个视图的 android:layout_weight 设置为 "1"。
这里以水平方向的均等布局来举例,垂直方向类似:
布局示例代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<!-- 比例 1: 1: 1 ,平均分配 -->
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#03A9F4"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="one"
android:textSize="50sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#8BC34A"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="two"
android:textSize="50sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#FF5722"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="three"
android:textSize="50sp" />
</LinearLayout>
布局显示效果:

# 不等分布
您也可创建线性布局,让子元素使用大小不同的屏幕空间:
- 如果有三个文本字段,其中两个声明权重为 1,另一个未赋予权重,那么没有权重的第三个文本字段就不会展开,而仅占据其内容所需的区域。另一方面,另外两个文本字段将以同等幅度展开,填充测量三个字段后仍剩余的空间。
- 如果有三个文本字段,其中两个字段声明权重为 1,而为第三个字段赋予权重 2(而非 0),那么现在相当于声明第三个字段比另外两个字段更为重要,因此,该字段将获得总剩余空间的一半,而其他两个字段均享余下的空间。
布局代码示例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical">
<!-- 比例 1 :1 :(内容适应)-->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#03A9F4"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="one"
android:textSize="50sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#8BC34A"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="two"
android:textSize="50sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#FF5722"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="three"
android:textSize="50sp" />
</LinearLayout>
<!-- 比例 1 :1 :2 -->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#03A9F4"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="one"
android:textSize="50sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#8BC34A"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="two"
android:textSize="50sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:background="#FF5722"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="three"
android:textSize="50sp" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
布局显示效果:

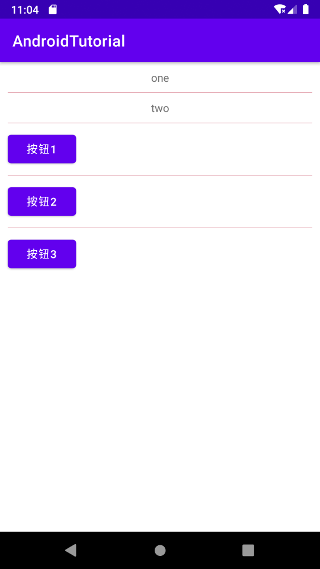
# 设置分割线
LinearLayout的 divider属性,可以为 LinearLayout 设置分割线 。
android:divider:设置分割线资源,可以是图片、drawable、color等资源。
android:showDividers:设置分割线的位置:none(无)、beginning(开始)、end(结束)、middle(每两个组件间) 。
dividerPadding:设置分割线的内边距 padding。
分割线布局代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:divider="@color/design_default_color_error"
android:dividerPadding="10dp"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:showDividers="middle">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:text="one" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:text="two" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:text="按钮1" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:text="按钮2" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:text="按钮3" />
</LinearLayout>
效果显示:
注意事项:
当 android:orientation="vertical" 时, 只有水平方向的设置才起作用,垂直方向的设置不起作用。 即此时只有:left,right,center_horizontal 是生效的。
当 android:orientation="horizontal" 时, 只有垂直方向的设置才起作用,水平方向的设置不起作用。 即此时只有:top,bottom,center_vertical 是生效的。
关于线性布局 LinearLayout 的介绍到这里就结束了,线性布局可以很好的在线性方向上(水平或者垂直)上进行相关的权重的布局,对于相对性的布局就有很大的局限性了,所以在开发中常见的用法就是使用其权重的特性来进行相关的界面布局。