上一节对 LinearLayout 进行了详细的解析,LinearLayout 也是我们用的比较多的一个布局,我们更多的时候更钟情于他的 weight(权重)属性,比例划分对屏幕适配还是帮助蛮大的;但是使用 LinearLayout 的时候也有很多的问题,就是当界面设计比较复杂的时候,需要嵌套多层的 LinearLayout,这样就会降低 UI Render 的渲染速度和效率。
如果使用 RelativeLayout(相对布局) 的话,可能仅仅需要一层就可以完成了,以父容器或者兄弟组件参考 + margin + padding 就可以设置组件的显示位置,还是比较方便的。相对布局其实通俗一点来说的话,可以理解是一个参考布局的方式,参考父布局或者同级组件的一个相对的参考位置,如:相对父布局的中间位置等。
注意:相对布局的
一个相对属性只会在一个方向上生效,一般都是使用多个不同方向属性来进行布局,最常用的就是同时使用水平和垂直方向的属性进行布局。
# 基本属性
- gravity:设置布局容器内的对齐方式。
- ignoreGravity:设置是否忽略 gravity 属性。
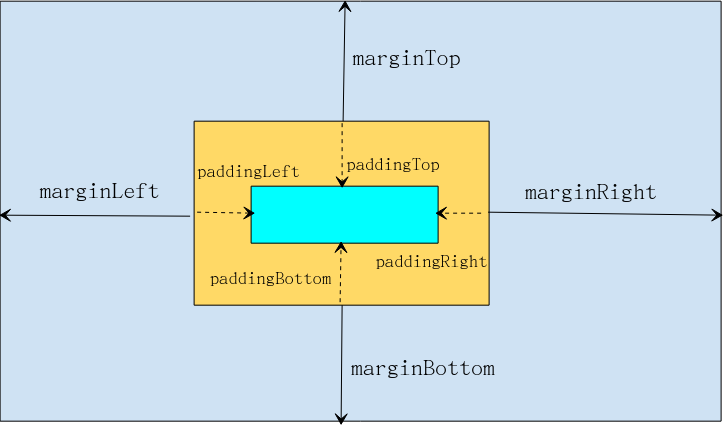
- layout_margin:设置组件的上下左右的外边距(组件与父容器的边距),与之对应的还分别有layout_marginLeft(左)、layout_marginTop(上)、layout_marginRight(右)、layout_marginBottom(下)等等单独方向的外边距属性。
- padding:设置组件的内边距(组件和内部元素之间的边距),与之对应的还分别有paddingLeft(左)、paddingTop(上)、paddingRight(右)、paddingBottom(下)等等单独方向的内边距属性。
margin 和 padding 属性是所有 View 相关组件的共通性属性,分别控制外边距和内边距,也有的人称 margin 是偏移,padding 是填充,其实无论怎么叫法,理解其中的含义和使用方法才是本质。
如果需要了解 RelativeLayout 的更多属性,请参考官方API (opens new window)。
margin 和 padding 理解示意图:
参考示例代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#5A5151">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="50dp"
android:layout_marginTop="300dp"
android:background="#00ddcc"
android:text="margin(left: 5dp, top: 300dp)" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#FFEB3B"
android:paddingLeft="50dp"
android:paddingTop="15dp"
android:text="padding(left: 50dp, top: 15dp)" />
</RelativeLayout>
示例运行效果:

# 根据父容器相对布局
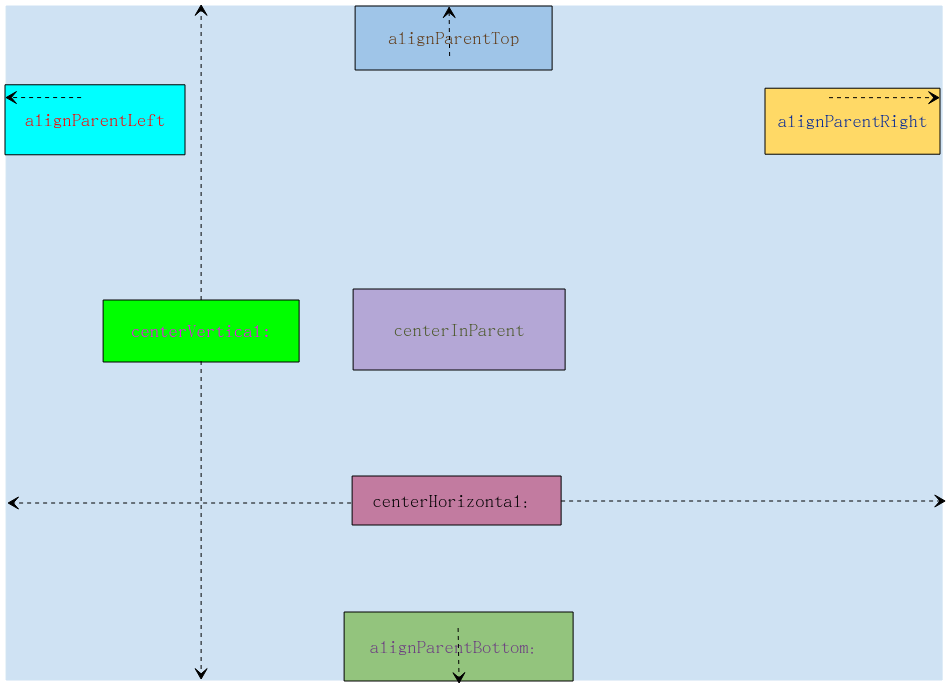
- layout_alignParentLeft:参考父布局左对齐。
- layout_alignParentTop:参考父布局顶部对齐。
- layout_alignParentRight:参考父布局右对齐。
- layout_alignParentBottom:参考父布局底部对齐。
- layout_centerHorizontal:参考父布局水平居中。
- layout_centerVertical:参考父布局垂直居中。
- layout_centerInParent:参考父布局的中间(水平和垂直居中)位置。
- layout_alignParentStart:当前配置是
LTR(从左到右,默认的阅读方式)时则等价 layout_alignParentLeft,如果是RTL(Right To Left是一种阿拉伯语、波斯语等情况下从右往左的阅读方式)时则等价 layout_alignParentRight。 - layout_alignParentEnd:当前配置是
LTR(从左到右,默认的阅读方式)时则等价 layout_alignParentRight,如果是RTL(Right To Left是一种阿拉伯语、波斯语等情况下从右往左的阅读方式)时则等价 layout_alignParentLeft。
理解示意图:
参考示例代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#5A5151">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_marginTop="30dp"
android:background="#FFEB3B"
android:text="alignParentLeft" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_marginTop="30dp"
android:background="#00ddcc"
android:text="alignParentRight" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="150dp"
android:background="#03A9F4"
android:text="alignParentTop" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="150dp"
android:background="#FF5722"
android:text="alignParentBottom" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:background="#cccccc"
android:text="centerInParent" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:background="#673AB7"
android:text="centerVertical" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="100dp"
android:background="#4CAF50"
android:text="centerHorizontal" />
</RelativeLayout>
示例运行效果:
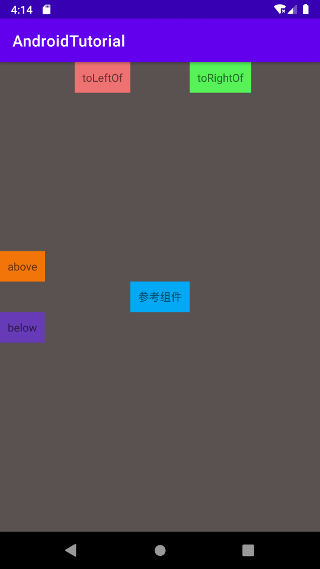
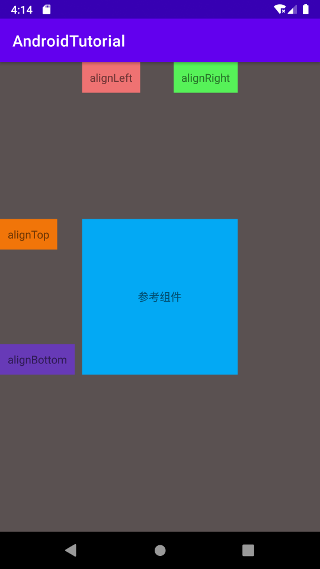
# 根据兄弟组件定位
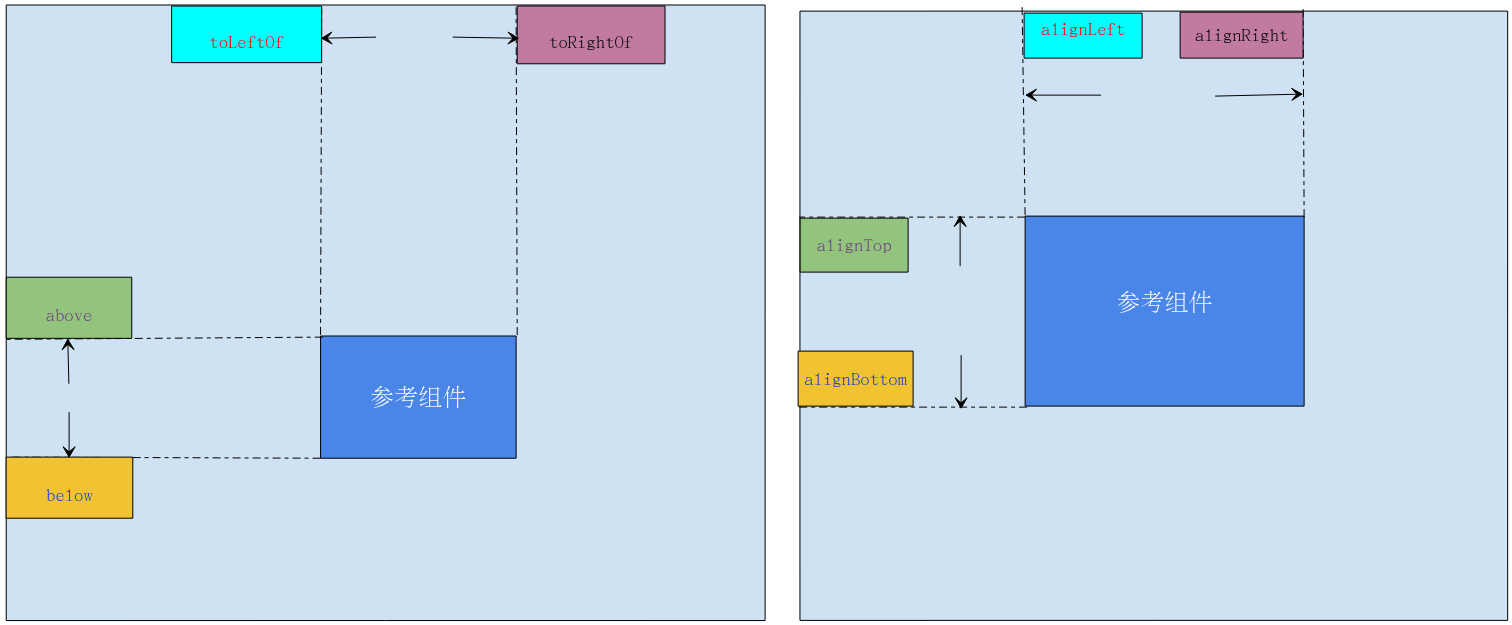
- layout_toLeftOf:参考组件的左边。
- layout_toRightOf:参考组件的右边。
- layout_above:参考组件的上方。
- layout_below:参考组件的下方。
- layout_alignLeft:对齐于参考组件的左边界。
- layout_alignRight:对齐于参考组件的右边界。
- layout_alignTop:对齐于参考组件的上边界。
- layout_alignBottom:对齐于参考组件的下边界。
兄弟组件:指的是布局中在
同一级节点中的组件。
理解示意图:
参考示例代码:
组件方向代码参考:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#5A5151">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_center"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:background="#03A9F4"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="参考组件" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/tv_center"
android:background="#EF7272"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="toLeftOf" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/tv_center"
android:background="#56F258"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="toRightOf" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_above="@id/tv_center"
android:background="#F17509"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="above" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/tv_center"
android:background="#673AB7"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="below" />
</RelativeLayout>
组件边界代码参考:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#5A5151">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_center"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:background="#03A9F4"
android:gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="参考组件" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignLeft="@id/tv_center"
android:background="#EF7272"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="alignLeft" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignRight="@id/tv_center"
android:background="#56F258"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="alignRight" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignTop="@id/tv_center"
android:background="#F17509"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="alignTop" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignBottom="@id/tv_center"
android:background="#673AB7"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="alignBottom" />
</RelativeLayout>
示例运行效果:
关于 RelativeLayout 的介绍就结束了,本节我们知道了利用相对布局组件中的相对参考的属性,可以进行更灵活和更方便的界面布局。